Models • TaskMatrix.AI
Overview
- “The amount of intelligence in the universe doubles every 18 months.” – Sam Altman, OpenAI CEO. This certainly seems to hold true for Microsoft’s TaskMatrix.AI.
- Microsoft has recently released TaskMatrix.AI which is a position paper on an AI ecosystem that connects foundation models with millions of APIs for task completion.
- TaskMatrix.AI is a mix of Toolformer and ChatGPT and is the future of LLMs.
- The use cases of TaskMatrix.AI are endless, from refining photographs, to controlling smart home devices, etc.; it can do more than was previously perceivable.
- TaskMatrix.AI intends to not only aid in the digital world, much like its predecessors such as ChatGPT, but also in the physical world by helping out with tasks. It does this by linking foundation models with existing models and APIs to serve a diverse variety of tasks.
- Per the paper below are the following tasks that TaskMatrix.AI can perform:
- “TaskMatrix.AI can perform both digital and physical tasks by using the foundation model as a core system to understand different types of inputs (such as text, image, video, audio, and code) first and then generate codes that can call APIs for task completion.
- TaskMatrix.AI has an API platform as a repository of various task experts. All the APIs on this platform have a consistent documentation format that makes them easy for the foundation model to use and for developers to add new ones.
- TaskMatrix.AI has a powerful lifelong learning ability, as it can expand its skills to deal with new tasks by adding new APIs with specific functions to the API platform.
- TaskMatrix.AI has better interpretability for its responses, as both the task-solving logic (i.e., action codes) and the outcomes of the APIs are understandable.”
TaskMatrix.AI Architecture
- The figure below (source) details the overall architecture for TaskMatrix.AI and the four key components it comprises, namely:
- Multimodal Conversational Foundation Model (MCFM): “which is responsible for communicating with users, understanding their goals and (multimodal) contexts, and generating executable codes based on APIs to accomplish specific tasks.”
- API Platform: provides a unified API documentation schema to store millions of APIs with different kinds of functions and allows API developers or owners to register, update, and delete their APIs.
- API Selector: recommends related APIs based on MCFM’s comprehension of the user command.
- API Executor: executes the generated action codes by calling the relevant APIs and return the intermediate and final execution results.
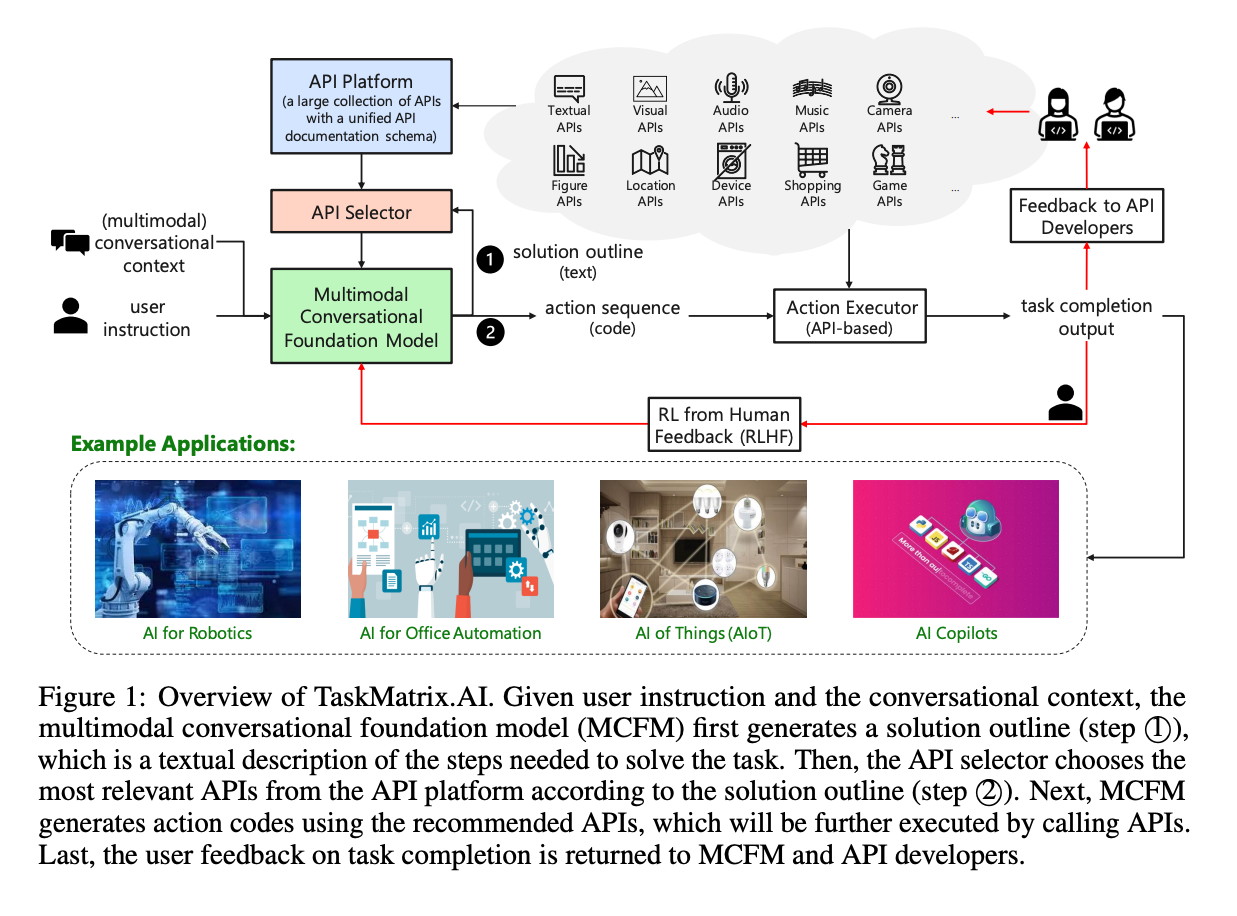
Multimodal Conversational Foundation Model (MCFM)
- MCFM has four inputs: the parameter of the foundation model, the API platform, the user instruction, and the conversational context. Using these inputs, the model generates action codes to accomplish the user’s instruction.
- Additionally, the ideal multimodal conversational framework model (MCFM) should have four main capabilities:
- Take multimodal inputs and generate executable codes based on APIs for specific tasks.
- Extract specific tasks from user instructions and propose solution outlines.
- Learn how to use APIs from their documentation and match them to specific tasks based on common sense and API usage history.
- Incorporate an explicit code verification mechanism to confirm reliability and trustworthiness.
- ChatGPT and GPT-4 are two examples of models that have these capabilities required for MCFM. However, GPT-4 is more suitable due to its ability for multimodal input.
API Platform
- The API platform has two main functions: storage of APIs and API management by developers or owners.
- The API platform has a unified API documentation schema consisting of five aspects for each API document:
- API Name: provides an abstract of the API and serves as an entry for the action executor.
- Parameter List: includes input parameters and return value, and each parameter has a name, description, data type, and default value.
- API Description: contains information about what the API does, how it works, inputs and outputs, and potential errors or exceptions.
- Usage Example (optional): demonstrates how the API can be used for complex APIs.
- Composition Instructions (optional): provides guidance on how to combine multiple APIs to accomplish complex user instructions.
- The example below is provided for opening a file:
API Name: open_local_file
API Parameter: (file_path:string, model:string="r"). file_path: string, the pathname (absolute or relative to the current working directory) of the file to be opened. mode: string
="r", the mode is an optional string that specifies the mode in which the file is opened. It defaults
to "r" which means open for reading in text mode. Other common values are "w" for writing. This
file will return a File object or OSError.
API Description: Open the file and return a corresponding file object. If the file cannot be opened,
an OSError is raised.
Usage Example: f = open_local_file("example.txt", "w")
Composition Instructions: Open should be used before reading and editing. The file should be
closed by close_local_file after all operations.
API Selector
- As we saw above, API selector aims to identify and choose the most apt API from the API platform that fits the task requirement best.
- API Selector aims to trim down the plethora of APIs the API platform may have by retrieving semantically relevant APIs.
- API selector can leverage module strategy to quickly locate relevant APIs.
- Module strategy refers to the approach of organizing APIs into specific packages or modules based on their domain. Each module corresponds to a specific area, such as visual models, math, specific software, or physical devices. By using this strategy, the API selector can quickly locate relevant APIs that fit the task requirement and solution outline as understood by MCFM. This approach helps to streamline the API selection process and makes it easier to retrieve semantically relevant APIs from the API platform.
Action Executor
- The action executor is designed to execute the action codes. TaskMatrix.AI uses an action executor to run various APIs, ranging from simple HTTP requests to complex algorithms or AI models that need multiple input parameters. (source)
- The action executer will also require a verification mechanism to enhance accuracy and reliability and confirm whether the outcome of the generated code fits the human-specified task.
Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF)
- TaskMatrix.AI will leverage RLHF to enhance MCFM and API selector inorder to offer better performance on complex tasks.
- RLHF will be used specifically to optimize the API selector using a trained reward model based on API feedback as in the below section.
Feedback to API Developers
- API developers will receive feedback on whether their API’s were used to complete the task or not.
- This will allow creating API documentation in the most optimal way to use given APIs.
Use cases of TaskMatrix.AI
- Now that we have seen the architecture, it’s time to see what tasks TaskMatrix.AI can help solve.
- Visual Task Completion is something TaskMatrix.AI would be able to perform since it is multimodal and capable of taking language and images as input. Let’s look at some visual tasks it can perform below:
- The image below shows how TaskMatrix.AI would build on top of VisualChatGPT and be able to better work with VQA tasks.
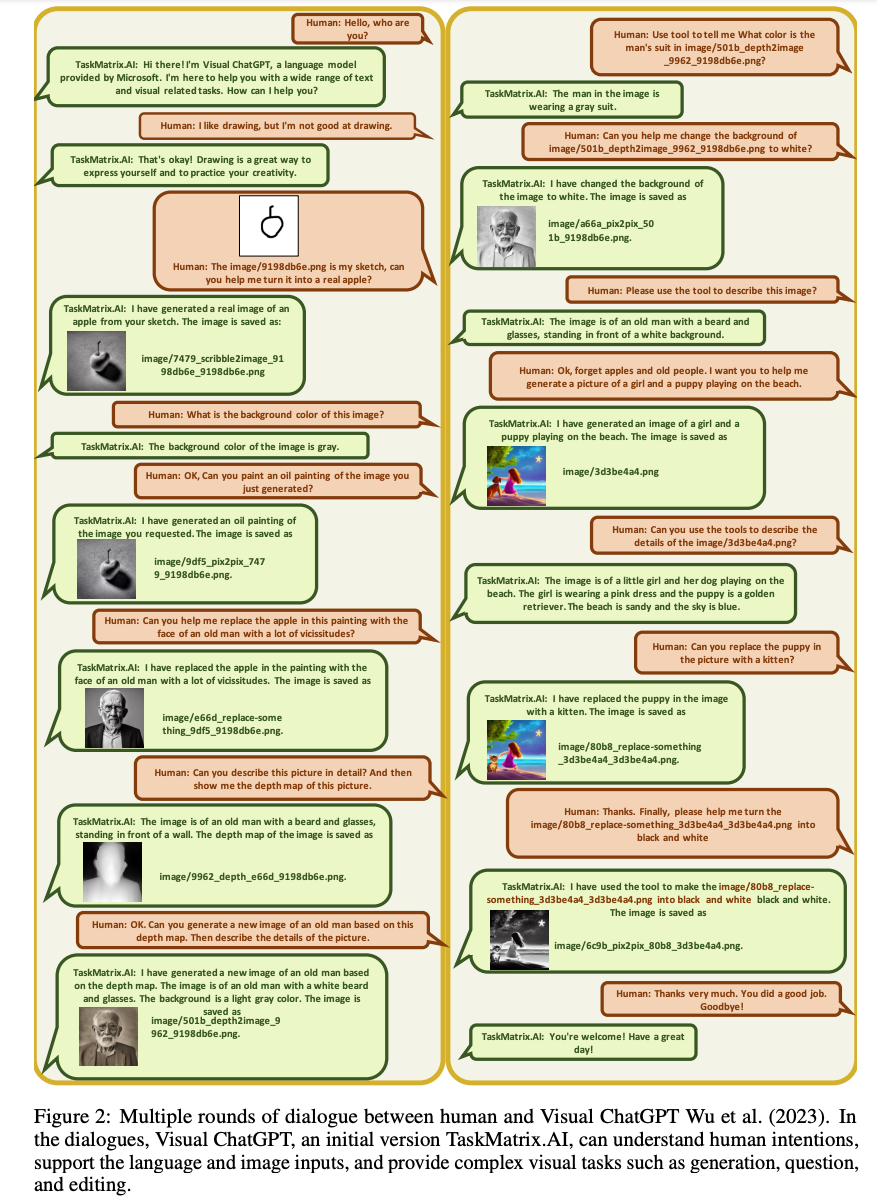
- Image editing, where it can remove or replace objects in an image will also be able to be facilitated with TaskMatrix.AI.
- Text-to-image where it generates an image from textual description.
- Image-to-Sketch/Depth/Hed/Line, where it can convert an image to a sketch, depth, Holistically-nested edge detection, or line using image processing techniques or computer algorithms.
- Sketch/Depth/Hed/Line-to-Image where it is the reverse of the above and will generate an image from the options given.
- The image below shows an example of how TaskMatrix.AI defines and executes on a solution outline using three API calls, Image Question Answering, Image Captioning, and Replace Objects from Image.

- Multimodal Long Content Generation
- Another use case of TaskMatrix.AI is to create large multimodal (images and text) content that removes the character limits that other models have.
- The example below, we can see how TaskMatrix.AI can take high level instruction from the user and generate a sensible response.

- Office Automation
- TaskMatrix.AI can easily reduce office workload by comprehending user instructions received via voice and automating the tasks.
- It can also work to use complex software without an immense amount of training which can allow the employees to focus on more pressing tasks.
- The example below, shows a conversation between TaskMatrix.AI and a person in the creation of PowerPoint slides by leveraging different APIs.

- Cloud services application
- TaskMatrix.AI can work as a smart home automation and talk to all the devices at home and work as a central connection point between them.
- The image below shows a conversation between a human and TaskMatrix.AI where it is leveraging both software and hardware of in-house robots to accomplish daily tasks.
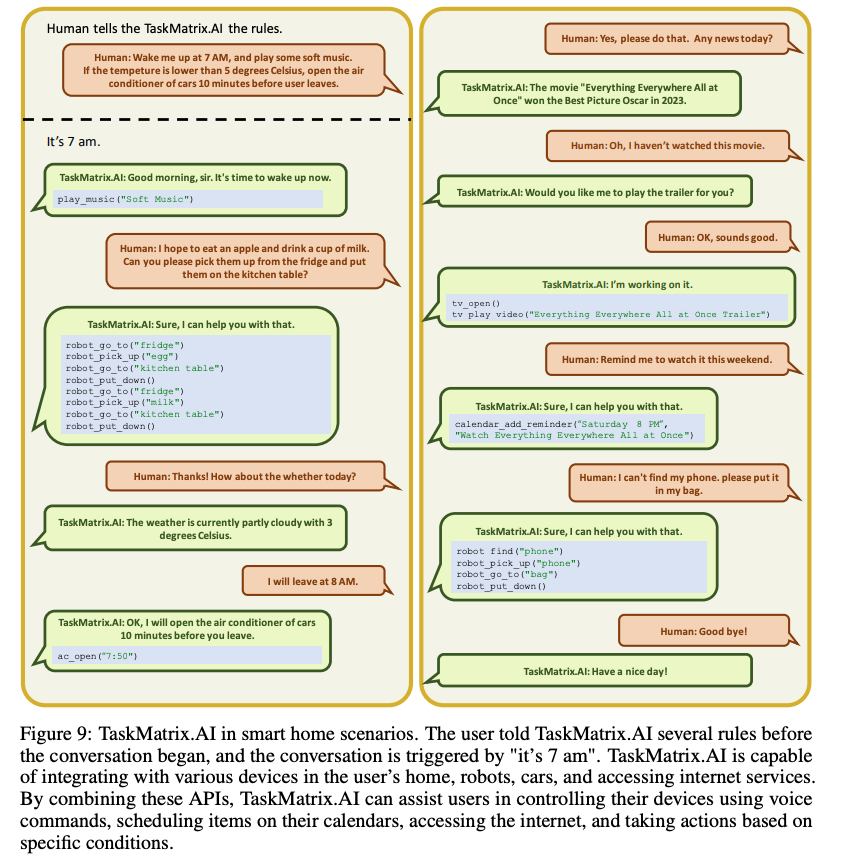
- Additionally, TaskMatrix.AI can be leveraged in a plethora of other scenarios with the only requirement being it can leverage APIs, such as accessing the Metaverse.
Challenges
- There are still quite a few drawbacks and limitations yet to be resolved and addressed with TaskMatrix.AI.
- For starters, the foundation model needs to be created that can handle various tasks, and various kinds of inputs, learn from human feedback, and use common sense reasoning to fulfill tasks to the highest quality.
- The plethora of APIs needs to be maintained on a platform with documentation and quality assurance which can be time-consuming as new APIs are created daily.
- Security and privacy can be a concern as the data sent to the model will need to be transferred to the APIs to retrieve relevant information.
Summary
- TaskMatrix.AI will be a platform for allowing humans to execute a vast amount of diversified tasks by leveraging foundation models and APIs.
- It will handle every ordinary tasks (say, creating PowerPoint slides or cleaning the house by running cleaning robots on a schedule) and make us more productive and creative.