Overview
- Visual ChatGPT: Talking, Drawing and Editing with Visual Foundation Models allows multimodal dialogue with users by interacting with ChatGPT using both text and image modalities.
- Visual ChatGPT builds on OpenAI’s ChatGPT as ChatGPT is not able to generate images at the current moment.
- On the other hand, Visual Foundation Models such as Stable Diffusion, are great at visual understanding, but cannot carry a conversation and end after one round of input/output.
- Visual ChatGPT, incorporating different Visual Foundation Models (VFMs), enables the user to interact with ChatGPT with a multimodal interface by:
- Sending and receiving not only language-based input but also images.
- Providing complex visual questions or visual editing instructions that require the collaboration of multiple AI models with multi-steps.
- Providing feedback and asking for corrected results.” (source).
- Another great upgrade Visual ChatGPT has done over ChatGPT is that it is publicly available here.
- Let’s dive into the details from the paper and key takeaways!
System Architecture
- The following diagram (source) shows the architecture and a sample set of examples:
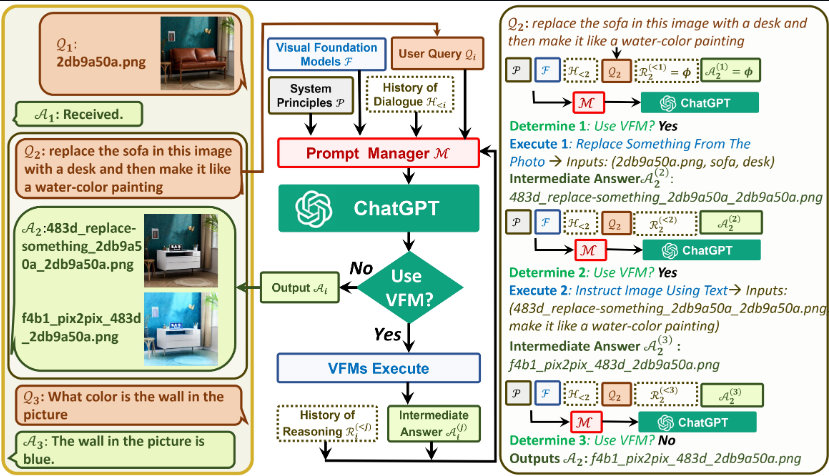
- An intuitive method to creating a system like Visual ChatGPT would be to train a multimodal conversation model with both text and images.
- The obvious drawbacks of this approach are the large computational resources it would use.
- Additionally, it would not be scalable for other modalities. We would have to resort to training it on every modality individually.
- Instead, the authors built Visual ChatGPT directly based on ChatGPT and incorporated a variety of VFMs.
- Let’s look at an example from the paper of how Visual ChatGPT works:
- A user uploads an image of a yellow flower and adds a difficult language instruction, such as “please generate a red flower conditioned on the predicted depth of this image and then construct it like a cartoon, step by step”
- Visual ChatGPT will initiate its VFMs via Prompt Managers.
- It will first render a depth estimation model to identify the depth information.
- Then, a depth-to-image model will create a figure of a red flower using the depth information.
- Finally, a style transfer VFM based on Stable Diffusion will transform the aesthetics of this image into a cartoon.
- This way, Visual ChatGPT is not re-inventing the wheel, but rather leveraging all of the technologies that currently exist to give an output.
- In order to shorten the gap between these VFMs and ChatGPT, the authors utilized Prompt Managers explained below.
Prompt Manager
- Prompt Managers are one of the key concepts that has come out of Visual ChatGPT.
- Here are the three key functions of Prompt Managers:
- Telling ChatGPT the capability of each VFM and specifying its respective input-output format.
- Converts different forms of visual information, for instance, PNG images, the depth images and mask matrix, to a textual form for ChatGPT to understand.
- Handles the histories, priorities, and conflicts of different VFMs.
- The following diagram (source) shows a zoomed-in view of the architecture and a sample of the VFMs supported:
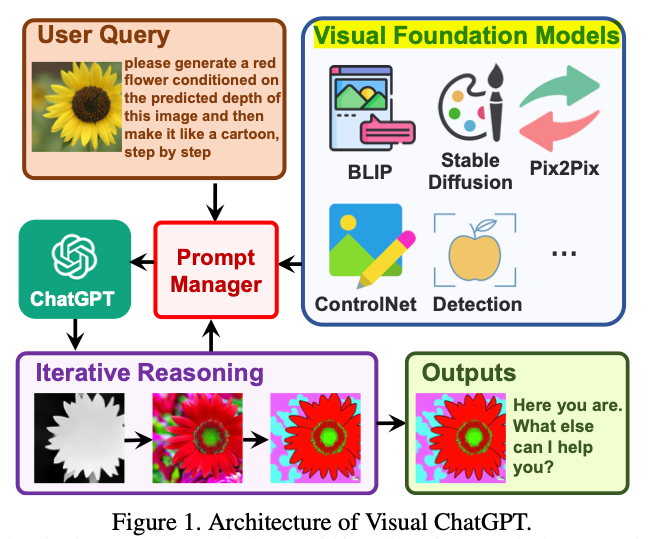
- Prompt Managers help Visual ChatGPT by giving information to ChatGPT from VFMs in an iterative fashion.
- Prompt Manager combines 22 different VFMs and defines the internal communication among them to streamline the user’s requested task.
- The following diagram (source) shows an overview of the prompt manager:
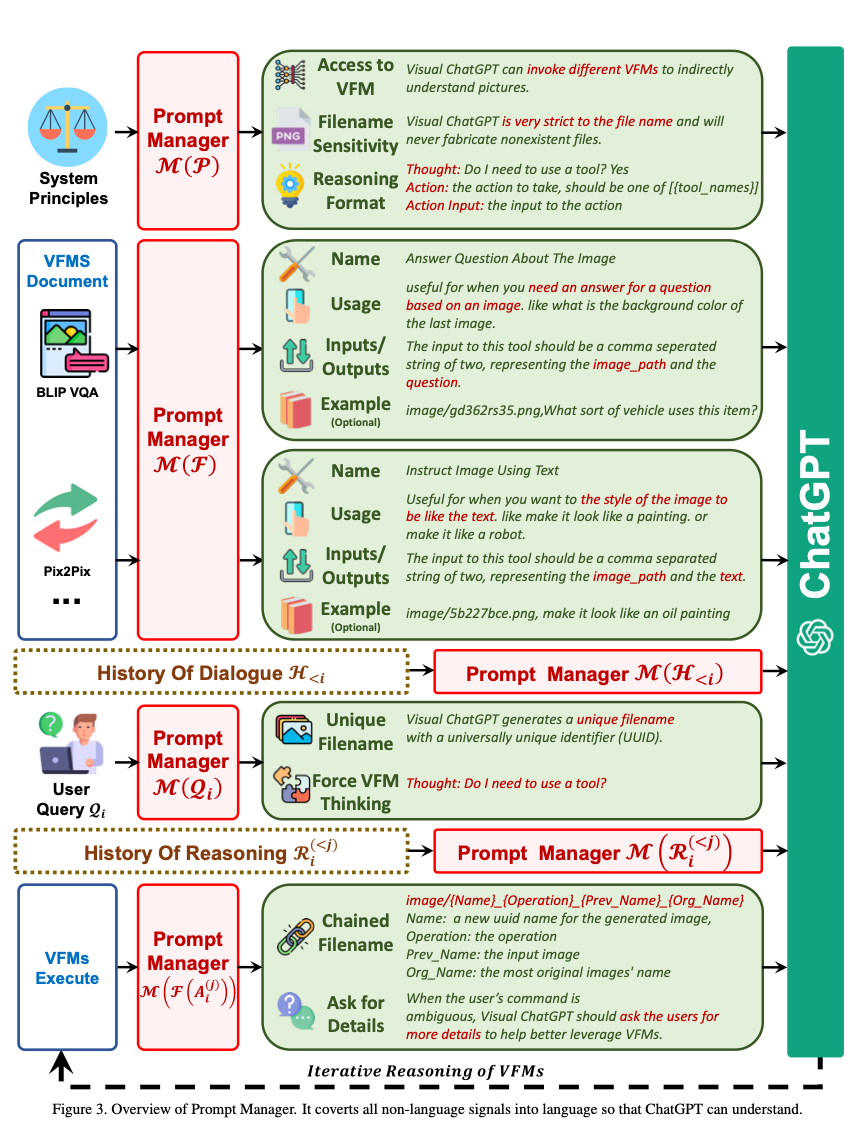
Managing VFMs
- Now let’s delve into how Prompt Manager manages the Foundation models.
- Visual ChatGPT interacts with multiple VFMs so the prompt manager needed an efficient strategy on how to best coordinate with VFM to use for which task.
- This is because different VFMs share similarities, like replacement of objects in image can be regarded as a generation of a new image. Or VQA task (image question answering) can be understood as offering a response according to the provided image.
- Thus, the need to distinguish the VFM’s became imminent.
- Below are the aspects Prompt Manager defines to help Visual ChatGPT accurately handle its VL task:
- Name: The name prompt helps Visual ChatGPT to understand the purpose of VFM in a concise manner and severs as the entry to VFM.
- Usage: The usage prompt describes the scenario where the VFM should be used.
- Input/Output: The input/output prompt defines the format of input and output required by the VFM.
- Example (optional): The example prompt is optional and as the name sounds, it gives an example to Visual ChatGPT which can be really helpful to better understand how a particular VFM works.
Handling Queries
- Visual ChatGPT supports many user queries and languages. It supports images as well, singular or multiple.
- In order to handle this, Prompt Manager uses the two aspects below:
- Generate Unique Filename:
- Visual ChatGPT handles two types of image queries: one where the image was uploaded and one where its a reference to an existing image.
- “For newly uploaded images, Visual ChatGPT generates a unique filename with a universally unique identifier (UUID) and adds a prefix string ”image” representing the relative directory, e.g.,
image/{uuid}.png (source).
- For queries about existing images, Visual ChatGPT ignores the filename check.
- Force VFM Thinking:
- The following suffix prompt is appended to the user query:
- “Since Visual ChatGPT is a text language model, Visual ChatGPT must use tools to observe images rather than imagination. The thoughts and observations are only visible for Visual ChatGPT, Visual ChatGPT should remember to repeat important information in the final response for Human. Thought: Do I need to use a tool?”
- The reasoning is two-fold provided below:
- It prompts Visual ChatGPT to use foundation models instead of relying solely on its imagination.
- It encourages Visual ChatGPT to provide specific out- puts generated by the foundation models, rather than generic responses such as “here you are” (source).
- The following diagram (source) shows an example of multiple rounds of dialogue between human and Visual ChatGPT:
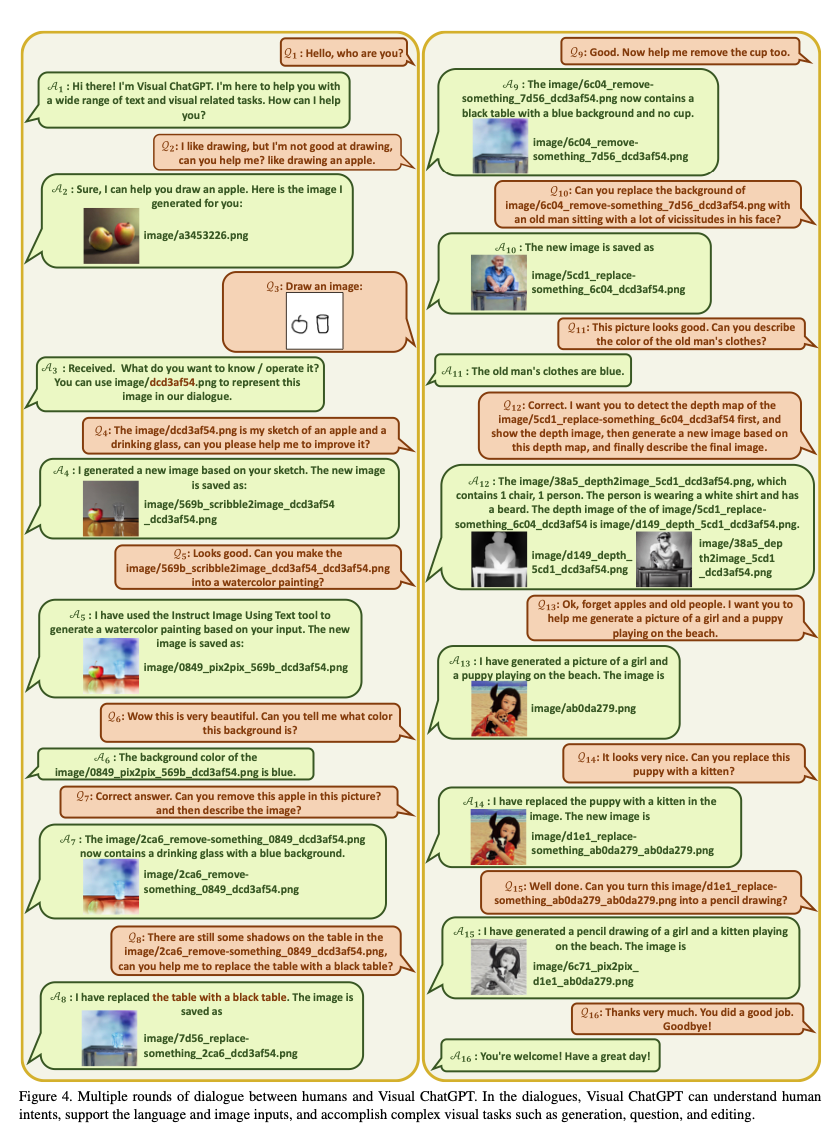
Limitations
- Event though Visual ChatGPT has built significantly on top of ChatGPT, however, a few limitations of Visual ChatGPT still remain.
- Visual ChatGPT is dependent on ChatGPT to assign tasks and on VFM to execute the tasks. Thus, it is limited by these models accuracies.
- Heavy prompt engineering is required by Visual ChatGPT to convert VFMs into language which can be time consuming.
- Limited real time capability as a prompt could invoke multiple VFMs, resulting in a delayed response time.
- The flexibility of easily plugging and unplugging foundation models may raise security and privacy concerns, particularly for remote models accessed via APIs.



